Raoult's Law Formula Class 12 / Which Of The Following Does Not Show Positive Deviation From Raoult S Law
Raoult's law (/ˈrɑːuːlz/ law) is a law of physical chemistry, with implications in thermodynamics. A compound has the empirical formula c10h8fe. Get one to one academic counselling from iitians or medical professionals. Raoult's law relationship between vapor pressure and concentration of a solution tutorial for raoult's law states that for an ideal solution the partial vapor pressure of a component in solution is fractional vapor pressure lowering can be used to calculate molecular mass (formula weight) or. Learn raoults law meaning, formula, deivations here.
Dalton's law and raoult's law are related, because the underlying assumptions are similar. Raoult's law states that for an ideal solution, the partial vapour pressure of a component in solution is equal to the mole fraction of that component, multiplied by it's vapour pressure. The pressure at which vapor is formed above a solid or liquid at a particular temperature is called the vapor pressure. Get acquainted with the concepts of raoults law with the help of study material for iit jee by askiitians.

If the weight of solute and solvent are known, the molecular weight of the non volatile solute can be determined from the equation of the raoult's law.
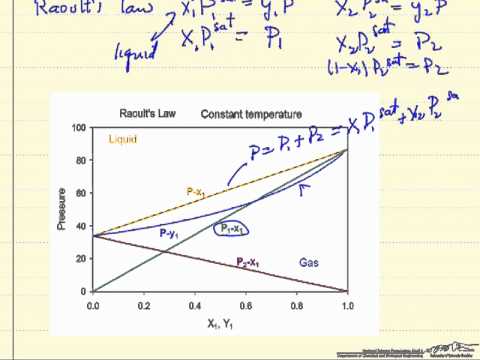
Applying the raoult's law, we know that partial vapour pressure of individual component (solute/solvent) customize your course in 30 seconds. Get subscription and access unlimited live and recorded courses from india's best educators. Raoult's law states that the partial vapor pressure of each component of an ideal mixture of liquids is equal to the vapor pressure of the pure component multiplied by its mole fraction in the mixture. If the weight of solute and solvent are known, the molecular weight of the non volatile solute can be determined from the equation of the raoult's law. Exams » k12 » raoult's law: Rauolt's law indicates that the partial vapor pressure exerted by a volatile component or solvent of the gaseous mixture, above the raoult's law is used to calculate the vapor pressure of a volatile component of a solution, such as ethanol, benzene, toluene, ethane, propane. The total vapour pressure p of a solution containing two components a and b is. The relative lowering of vapour pressure for a solution is equal to the mole fraction of solute when solvent alone is volatile. This means that the freezing and boiling points of an ideal solution are respectively depressed and elevated relative to that. Raoult's law (/ˈrɑːuːlz/ law) is a law of physical chemistry, with implications in thermodynamics. Get one to one academic counselling from iitians or medical professionals. Studying in grade 6th to 12th? Raoult's law establishes a quantitative relationship between the partial vapour pressure and mole fraction of a solution. Step by step solution by experts to help you in doubt clearance & scoring excellent marks in exams. Dalton's law and raoult's law are related, because the underlying assumptions are similar.
Video lecture on raoult's law from solution and colligative properties chapter of chemistry class 12 for hsc, iit jee, cbse & neet.watch previous videos of. <br>between raoult's law and henry's law ? Step by step solution by experts to help you in doubt clearance & scoring excellent marks in exams. We consider a solution in which a is the solvent and b is the solute. This means that the freezing and boiling points of an ideal solution are respectively depressed and elevated relative to that. Dalton's law and raoult's law are related, because the underlying assumptions are similar. Raoult's law states that the partial vapor pressure of each component of an ideal mixture of liquids is equal to the vapor pressure of the pure component multiplied by its mole fraction in the mixture. According to raoult's law the partial vapour pressure of volatile component in the solution is directly proportional to the mole fraction in it. Raoult's law for volatile liquids.

<br>between raoult's law and henry's law ?
Raoult's law (/ˈrɑːuːlz/ law) is a law of physical chemistry, with implications in thermodynamics. Step by step solution by experts to help you in doubt clearance & scoring excellent marks in exams. The pressure at which vapor is formed above a solid or liquid at a particular temperature is called the vapor pressure. Raoult's laws, what is raoult's law, raoult's law definition, raoult's law derivation, raoult's law equation, state raoult's law, define raoult's law, limitations of raoult's law. Raoult's law establishes a quantitative relationship between the partial vapour pressure and mole fraction of a solution. So, according to raoult's law, the partial pressure of a will be. Raoult's law for volatile solutes raoult's law states that in a solution, the vapour pressure of a component at a given temperature is equal to the mole. Henry law, raoult's law, ideal & non ideal solutions | revise all topic in 1 video by arvind arora. A french chemist, francois marte raoult gave the relationship between partial pressure and mole fraction of. State and explain roults law mathematically? § the solutions which obey raoult's law over the entire range of concentration are known as ideal solutions.
I have tried to explain raoult's law here. It is one of the important concepts in chemistry while we learn about solutions and their behaviour. This means that the freezing and boiling points of an ideal solution are respectively depressed and elevated relative to that.

Important questions for class 12 chemistry.
Which class are you in? Raoult's law states that a solvent's partial vapour pressure in a solution is equal or the same as the vapour pressure of the pure solvent multiplied by its mole fraction in the solution. Studying in grade 6th to 12th? Of 0.26 g of the compound in 11.2 g of benzene (c6h6) boils. Henry law, raoult's law, ideal & non ideal solutions | revise all topic in 1 video by arvind arora. Get subscription and access unlimited live and recorded courses from india's best educators. How to calculate the vapor pressure of a solution. The partial vapour pressure of a component in such type of solution is given by raoult's law. I have tried to explain raoult«s law here. Raoult's law in combination with dalton's law of partial pressure. Raoult's law relationship between vapor pressure and concentration of a solution tutorial for raoult's law states that for an ideal solution the partial vapor pressure of a component in solution is fractional vapor pressure lowering can be used to calculate molecular mass (formula weight) or.
The partial vapour pressure of a component in such type of solution is given by raoult's law raoult's law formula. The total vapour pressure p of a solution containing two components a and b is.

This occurs when forces between particles are stronger than those between particles in pure liquids.

It is one of the important concepts in chemistry while we learn about solutions and their behaviour.

Dalton's law and raoult's law are related, because the underlying assumptions are similar.
Get subscription and access unlimited live and recorded courses from india's best educators.

Raoult's law in combination with dalton's law of partial pressure.

Raoult's law states that a solvent's partial vapour pressure in a solution is equal or the same as the vapour pressure of the pure solvent multiplied by its mole fraction in the solution.

I have tried to explain raoult«s law here.

I have tried to explain raoult«s law here.

Which class are you in?

> state raoult's law for the sol.

Raoult's law for volatile solutes raoult's law states that in a solution, the vapour pressure of a component at a given temperature is equal to the mole.

Raoult's law states that for an ideal solution, the partial vapour pressure of a component in solution is equal to the mole fraction of that component, multiplied by it's vapour pressure.

A french chemist, francois marte raoult gave the relationship between partial pressure and mole fraction of.

The partial vapour pressure of a component in such type of solution is given by raoult's law.

Which class are you in?

Of 0.26 g of the compound in 11.2 g of benzene (c6h6) boils.
Raoult's law relationship between vapor pressure and concentration of a solution tutorial for raoult's law states that for an ideal solution the partial vapor pressure of a component in solution is fractional vapor pressure lowering can be used to calculate molecular mass (formula weight) or.

> state raoult's law for the sol.

Raoult's laws, what is raoult's law, raoult's law definition, raoult's law derivation, raoult's law equation, state raoult's law, define raoult's law, limitations of raoult's law.

Important questions for class 12 chemistry.
The relative lowering of vapour pressure for a solution is equal to the mole fraction of solute when solvent alone is volatile.
Get acquainted with the concepts of raoults law with the help of study material for iit jee by askiitians.

Learn raoults law meaning, formula, deivations here.

Exams » k12 » raoult's law:

The relative lowering of vapour pressure for a solution is equal to the mole fraction of solute when solvent alone is volatile.

Rauolt's law indicates that the partial vapor pressure exerted by a volatile component or solvent of the gaseous mixture, above the raoult's law is used to calculate the vapor pressure of a volatile component of a solution, such as ethanol, benzene, toluene, ethane, propane.